Organ systems are a group of organs that work
together for one goal.
The human body is composed of approximately 75 trillion cells
that always works, has the task of each, and can work both with an
outstanding management system.
The human brain is composed
of approximately 10
billion complex, but great work together and knows each task,
as well as work automatically with the speed which is
pretty amazing. The brain regulates automatically how the
heart has to beat, your lungs take oxygen from
the air, regulate the digestive system, release digestive
enzymes it needs with the right amount of time incoming food,
regulate the body's defense system against disease, and
more. Everything works automatically with a regular rhythm.
Several organs can be part of more than one system: for
example, the pancreas is part of the digestive and endocrine systems in
mammals. Although the details may vary, all mammals, including
humans, have the same organ system, ten in terms
of function: digestive, circulatory, respiratory, urinary, nerve, muscle, bone, reproduction,
endocrine and integumentary.
Some organs work together to form organ
systems, there are many organ systems in the human machine,
among other things:
The Respiratory System
Consists of the respiratory tract, from the nasal
cavity, larynx, and lungs. Its function is to place the oxygen
into the bloody and pull out the remaining substance metabolism
are carbon dioxide and water vapor to the outside of the
body.
This system allows the body to absorb oxygen – needed
to extract energy from food –and to expel carbon
dioxide, which is a byproduct of this process which should not
reach levels toxic. The respiratory system consists of the
lungs and Airways. Air duct is divided again over and over in
each lung, the alveoli at the end – a small cavity of the
oxygen absorbed by red blood cells, and where the flow of
carbon dioxide, which will be issued when the animal breathed out.
The circulatory system
Consists of the heart, blood vessels, blood and lymphatic circulatory
system.
The circulatory system functions that are
responsible for transporting nutrients and oxygen throughout the
body to where they are needed, and to protect the body
against disease-causing organisms. Both functions are
sometimes classed separately as the lymphatic and cardiovascular
system, respectively. Cardiovascular organs are the heart,
blood vessels, and blood. The lymphatic system involving glands such
as the spleen and thymus, which generate or modify cells called lymphocytes that are
released into the bloodstream and destroy harmful organisms.
The System excretion
Digestion, and others, is the process in which the
body produces a number of waste materials that is released into
the blood stream, and will accumulate to produce a number
of toxic if not removed. Excretion system, which
consists of the kidneys, bladder, and a connecting tube, provides
the means to remove these substances.
This system organizes the global residual substances outside
the body metabolism: urine is issued via the kidneys; perspiration secreted through
the skin; bile secreted by the liver; carbon dioxide gas and water
vapor expelled through respiration.
In addition, there is also a residual substance expenses the
gut in the form of the stool that is expelled through the anus. Excretion system
functions are important because the substance could poison the
rest of the body if not removed.
The Digestive System
Consists of the digestive tract, from the mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, colon, intestine, anus to the SINKHOLE. In addition, the digestive system is also aided by the gland-gland that AIDS digestion, such as salivary gland, pancreas gland, and the liver produces bile. Functions of the digestive system are to prevent the food that goes into a meal offering that will be used by the body.
The function of this organ system is to change the essential nutrients in the food into a form that can be absorbed by the body. The digestive system consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver and intestines. After the food has been chewed, it goes into the stomach, where the enzymes that digest the proteinuria are released, then into the intestine, where nutrients are absorbed. Absorption is aided by a liquid secreted by the pancreas and the liver, which helps in the breakdown of carbohydrates and fats.
Skeletal System
As the name suggests, this system is basically the framework, although it also includes the ligaments and cartilage. The most obvious function of the bone to form this framework is to provide support for the body, but they also help protect vulnerable organs and serves as a lever for skeletal muscle pull something. Other functions, still less obvious, is the production of blood cells in the bone marrow, and storage of essential minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, which can be released when needed.
The nervous system
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal
cord, nerves and sensory organs. Its function is
twofold. First, it allows external stimuli, such as sights,
sounds, smells and sensations to the sensory organs are conveyed
from the brain, where they are interpreted. Second, it allows a
signal to be sent from the brain through the spinal cord
and nerves, muscles, causing them to move as directed.
There are two types of the nervous system, namely:
The autonomic nervous system, which works automatically without
being able to consciously ruled, for example setting of
breathing, heart rate, digestion of food, enzyme, hormone production, and
so on. The autonomic nervous system is the key to Automation machine the
human body.
The motor nervous system could consciously rule,
for example, muscle-skeletal muscle can we order for driven where and what
it looks like.
The muscular system
Muscle is composed of, a long thin cells can contract causes movement. The
muscular system involves three types of muscles: skeletal,
cardiac and smooth muscle.
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle under conscious control, and
moving when directed to do so by the brain.
Heart Muscle
Just in the heart of autonomous work,
also without being able to consciously rule.
Smooth Muscle
Found in the organs of the body such as the
intestines, blood vessels, lung, and others. This muscle can
be ruled without autonomous working consciously.
The endocrine system
This system is related to the production of various hormones that maintain the body chemistry and affect many body functions. It is controlled by the hypothalamus gland in the brain, but it involves a lot of other organs, including the thyroid gland, the pituitary gland, kidneys and pancreas. Hormones are produced by the endocrine system affect the growth, sexual development, the absorption of water and energy consumption, among others.
This system serves to produce the hormone hormones that regulate growth and balance of fluids and electrolytes the body systems. The endocrine system is made up of, the pituitary gland located at the base of the cerebrum and is the largest gland as an activity of other glands, mammary glands, son of mumps mumps, glandular childkidney, pancreas glands, genital glands, thymus gland's DNA.
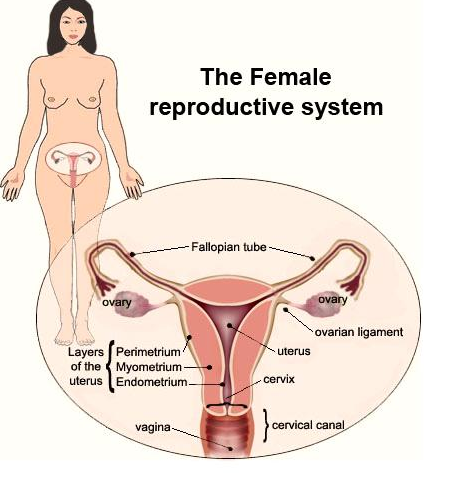
The Reproductive System
The reproductive system is related to the
production of cells that come together to form a new organism, by
creating the possibility of fertilization of the egg cell,
and by ensuring the development of secure early offspring. Organs differ
between men and women.
In men, the main ones are the testes, prostate and
penis, while in women, the major organs are the ovaries,
uterus and vagina. The ovaries produce eggs that are fertilized
by male sperm, produced in the testes. The embryo then develops inside the
womb or uterus.
Integumentary system
The system integument or covering is better
known as skin, hair and nails. Its functions to protect the
body from injury, water loss and infections; to prevent excess
heat by producing sweat; and to create vitamin D, which is
produced in response to sunlight. Hair also keeps the body warm in
cold weather.








0 Response to "Systems of the human body and its functions"
Post a Comment